Describe How a Plasmid Can Help a Cell
Scientists can force bacteria to keep them. The classic example of plasmid vector is pBR322 which was one of the first such vectors to be.
Plasmids And Co Selection Antibiotic Resistance React
Some bacteria are antibiotic resistant.

. Now the two open ends of linear plasmid are joined to the ends of the foreign DNA. Often the genes carried in plasmids provide bacteria with genetic advantages such as antibiotic resistance. Describe plasmid modification 8 points maximum.
In addition the plasmid can have a marker gene as the visual marker to help determine whether cloning was successful. Describe how a plasmid can be genetically modified to include a piece of foreign DNA that alters the phenotype of bacterial cells transformed with the modified plasmid. They are not essential for the bacterium but may confer a selective advantage.
The size of the plasmid DNA is generally 1kb to 2 kb used in genetic research the smaller size of it makes it easy to create and modify for genetic engineering. Isolate them such as with alkaline lysis. One class of plasmids colicinogenic or Col factors determines the production of.
Ecoli DNA is re-inserted into bacterial cell to reproduce human insulin. It can be avoided b y immobilizing the cells and staining them with dyes. Plasmid DNA from Ecoli is removed and restriction enzymes are used to cut DNA.
A plasmid is a small extrachromosomal DNA molecule within a cell that is physically separated from chromosomal DNA and can replicate independently. Using both text and a diagram you create describe and explain how a plasmid can be involved in transporting bacterial chromosomal genes from one mature bacterial cell to another mature bacterial cell and how those donated chromosomal genes can become incorporated into the recipient cells chromosome. R plasmids can also carry the tra.
Virtually all plasmids that are used to deliver DNA contain genes for antibiotic resistance. Many plasmids code for the production of one or more enzymes that destroy certain anitbiotics enabling the organism to resist the otherwise lethal effect of these medications. Once bacteria have been treated with a plasmid scientists grow them in the presence of antibiotic.
While this is a serious health problem it. Plasmids are circular deoxyribonucleic acid DNA molecules that replicate independently of the bacterial chromosome. Plasmids are small circular molecules of double-stranded DNA derived from larger plasmids that occur naturally in bacteria.
Human DNA with insulin is also cut and inserted into the Ecoli plasmid. Mutagenesis is easily accomplished by using. The transformed cells are selected by the antibiotic resistance of the used plasmid.
Produce proteins that glow so that scientists can track their location or quantity inside a cell. Describe how a plasmid can be genetically modified to include a piece of foreign DNA that alters the phenotype of bacterial cells transformed with the modified plasmid. The cleavage converts the circular plasmid DNA into a linear DNA molecule.
The ideal plasmid vectors have high copy numbers inside the cell. The cells repel the negatively charged dye allowing the colorless cells to stand out against the background. Transformation of Bacterial Cells with Plasmid DNA Introduction.
Mutate them using restriction enzymes ligation enzymes and PCR. Human insulin is then isolated and used to treat diabetics. A bacterium with an R plasmid for penicillin resistance is able to survive treatment by that antibiotic.
Acidic dyes do not stain cells this is a procedure that colors the background. As such it ensures high numbers of the target gene for cloning purposes. 69 All of the enzymes required for replication of the plasmid DNA are produced by a host bacterium.
Plasmids play crucial roles in genetic engineering molecular cloning and various areas of Biotechnology. Describe a procedure to determine which bacterial cells have been successfully transformed. Biology questions and answers.
Presence of selectable marker. Using both text and a diagram you create describe and explain how a plasmid can be involved in transporting bacterial chromosomal genes from one mature bacterial cell to another mature bacterial cell and how those donated chromosomal genes can become incorporated into the recipient cells chromosome. Plasmids can be constructed artificially artificial plasmids are called vectors and are used to introduce foreign DNA into another cell of interest.
Some of the many things that plasmids can be used to do include. Describe a procedure to determine which bacterial cells have been successfully transformed. Plasmids are used in genetic engineering to transfer foreign genetic material into different types of cells.
Transformation refers to the process in which the cell integrates foreign DNA to its genetic code meaning it takes the genes and incorporates them into the cells current DNA. Cells that can do this naturally most commonly bacteria and archea are known as competent. Select them using genetic markers.
Only those cells that contain the plasmid will survive grow and reproduce. 68 Most plasmid-cloning vectors are designed to replicate inE. The plasmid is a self-replicating element that is inherited in each bacterium during cell division.
Topic Description 1 point each. Coli do not have high. However plasmids are sometimes present in archaea and eukaryotic organisms.
Plasmids are used to prepare recombinant DNA with the desired gene to transfer genes from one organism to another. This is known as genetic engineering. This also ensures that the gene of interest is increased during genomic division.
Produce large amounts of a protein so that scientists can purify and study it in a controlled setting. In nature plasmids often carry genes that. Plasmids naturally exist in bacterial cells and they also occur in some eukaryotes.
They are most commonly found as small circular double-stranded DNA molecules in bacteria. Plasmid in microbiology an extrachromosomal genetic element that occurs in many bacterial strains. Also the stability of the plasmid DNA is very high.
Plasmids carrying a specific gene are introduced into bacterial cells which multiply rapidly and the required DNA fragment is produced in larger quantities. The plasmid vector is isolated from the bacterial cell and at one site by restriction enzyme. Describe how a plasmid can help a cell.
Most plasmid vectors encode a gene that confers bacterial resistance to antibiotic. This origin permits the efficient replication of plasmid to a large number of copies of cells by the plasmids replicon a region of approximately 1000 bp encoding the site at which DNA replication is initiated. Describe how a plasmid can help a cell.
The foreign DNA fragment is inserted into the plasmid and the recombinant DNA molecule is transformed into the recipient cell.

10 3 Plasmids Are Easily Isolated From Bacterial Cells Biology Libretexts

Insertion Of A Plasmid Vector Into A Bacterial Cell Teaching Biology Microbiology Study Biology College
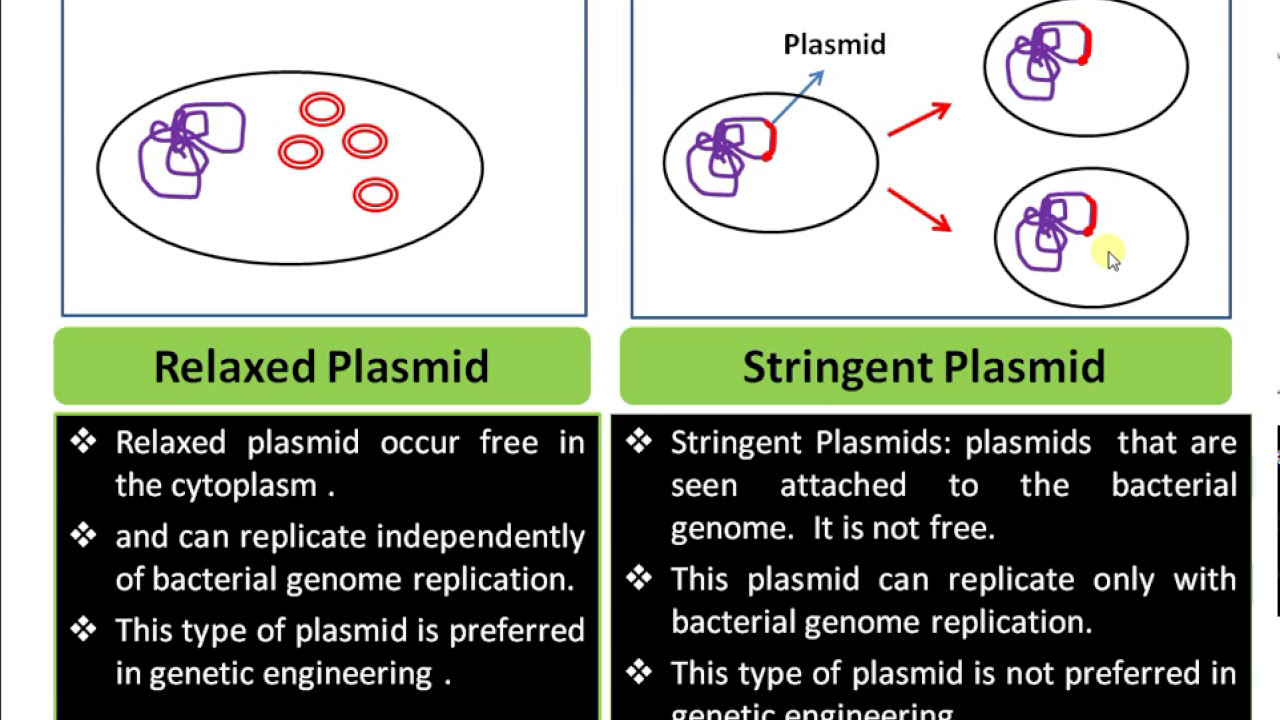
Definition Of Plasmid Relaxed Plasmid Vs Stringent Plasmid Functions Of Plasmid In Bacterial Cell Youtube

Comments
Post a Comment